WASHINGTON — She is an American professional basketball star, accused of carrying hashish oil in her luggage.
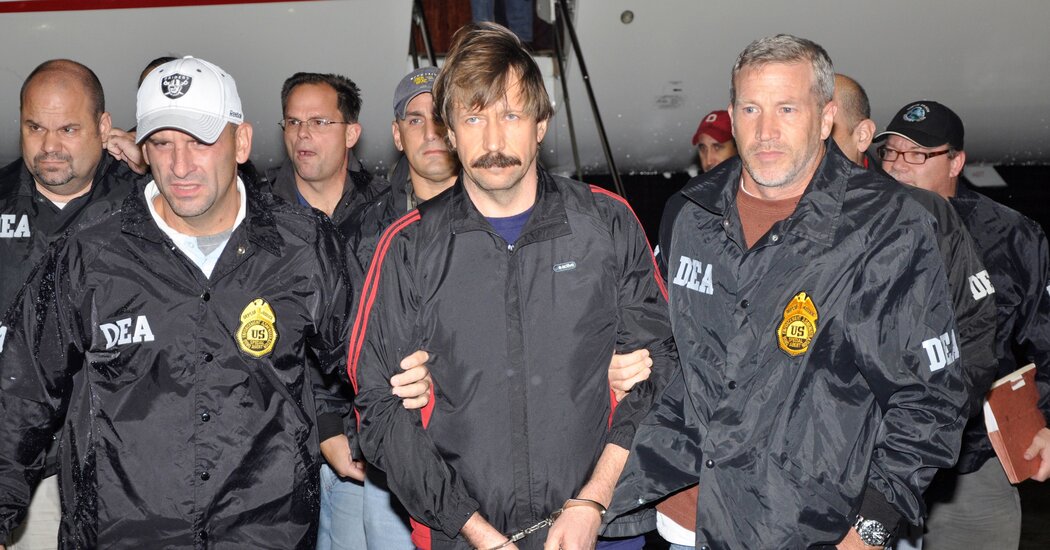
He is a notorious Russian arms dealer known as the “Merchant of Death,” serving a 25-year federal prison sentence for conspiring to sell weapons to people who said they planned to kill Americans.
And the Kremlin appears interested in linking their fates, in a potential deal with the Biden administration that would free both.
The vast disparity between the cases of Brittney Griner and Viktor Bout highlights the extreme difficulty President Biden would face if he sought a prisoner exchange to free Ms. Griner, the detained W.N.B.A. player, from detention in Moscow. The Biden administration, reluctant to create an incentive for the arrest or abduction of Americans abroad, would be hard-pressed to justify the release of a villainous figure like Mr. Bout.
At the same time, Mr. Biden is under pressure to free Ms. Griner, who was arrested at a Moscow-area airport in February and whom the State Department classified in May as “wrongfully detained.” That reflects concern that the Kremlin considers her leverage in the tense confrontation between the United States and Russia over Ukraine. Last week, dozens of groups representing people of color, women and L.G.B.T.Q. Americans sent a letter urging Mr. Biden to “make a deal to get Brittney back home to America immediately and safely.”
Ms. Griner’s trial was scheduled to start on Friday.
Mr. Bout, 55, a former Soviet military officer who made a fortune in global arms trafficking before he was caught in a federal sting operation, could be the price for any deal. Russian officials have pressed Mr. Bout’s case for years, and in recent weeks Russian media outlets have directly linked his case to Ms. Griner’s. Some, including the state-owned Tass news service, have even claimed that talks with Washington for a possible exchange are already underway, something that U.S. officials will not confirm.
Mr. Bout’s New York-based lawyer, Steve Zissou, said in an interview that Russian officials are pressing to free Mr. Bout, who was convicted in 2011 of offering to sell weapons, including antiaircraft missiles, to federal agents posing as members of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, or FARC. Mr. Zissou said that he met with Anatoly I. Antonov, Russia’s ambassador to the United States, in June in Washington and that Mr. Antonov told him the release of Mr. Bout was a very high priority for the Russian government.
“It has been communicated to the American side very clearly that they’re going to have to get real on Viktor Bout if they expect any further prisoner exchanges,” Mr. Zissou said. “My sense of this is that no American is going home unless Viktor Bout is sent home with them.”
U.S. officials have declined to substantiate that notion and won’t discuss any potential deal to free Ms. Griner. The State Department as a matter of practice dismisses questions about prisoner exchanges around the world, warning that they set a dangerous precedent.
“Using wrongful detention as a bargaining chip represents a threat to the safety of everyone traveling, working and living abroad,” the department’s spokesman, Ned Price, recently said.
Better Understand the Russia-Ukraine War
Mr. Biden did agree to a prisoner exchange in April, in which Russia released Trevor Reed, a former U.S. Marine from Texas who had been held since 2019 on charges of assaulting two police officers. The United States in return freed Konstantin Yaroshenko, a pilot sentenced in 2011 to 20 years in prison for drug smuggling. But White House officials stressed that Mr. Reed’s failing health made his case exceptional.
Many people have expressed support for Ms. Griner, a star athlete and basketball icon. Less obvious is the Russian government’s solidarity with an organized crime titan linked to terrorists and war criminals. In December, a government building in Moscow exhibited two dozen of Mr. Bout’s pencil sketches and other artwork produced from his cell in a federal penitentiary building near Marion, Ill.
By the time of his arrest in 2008, Mr. Bout (pronounced “boot”) was so known that an arms-trafficking character played by Nicolas Cage in the 2005 film “Lord of War” was based on his life.
Born in Dushanbe, Tajikistan, he attended a Russian military college and served as a Soviet air force officer.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Mr. Bout began making money ferrying cargo between continents. U.S. officials say he soon became one of the world’s top arms dealers, transporting weapons from the former Soviet military in Ilyushin transport planes, with a particularly lucrative business in war-torn African countries like Liberia and Sierra Leone. Mr. Bout denies that he knowingly trafficked arms.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the United States and European nations were sure that Mr. Bout’s weapons shipments were not only fueling death and misery but also violating United Nations arms embargoes. They were particularly alarmed by intelligence suggesting he may have done business with the Afghan Taliban and even Al Qaeda, charges he denies.
Eventually, the United States lured Mr. Bout into a trap. In 2008, a pair of Drug Enforcement Administration agents posing as members of Colombia’s leftist FARC rebel group arranged a meeting in Bangkok with Mr. Bout to buy weapons including 30,000 AK-47 rifles, plastic explosives and surface-to-air missiles for use against Colombia’s government and the American military personnel supporting its campaign against the FARC.
“Viktor Bout was ready to sell a weapons arsenal that would be the envy of some small countries,” Preet Bharara, then the U.S. attorney for the Southern District of New York, said after his conviction. “He aimed to sell those weapons to terrorists for the purpose of killing Americans.”
The FARC’s official status at the time as a foreign terrorist organization meant that Mr. Bout drew a mandatory federal minimum sentence of 25 years.
One former U.S. official familiar with Mr. Bout’s situation said the Russian government’s interest in his freedom appeared to be personal and that he has ties to powerful people close to President Vladimir V. Putin.
Another former American official pointed to a somewhat more principled reason: Mr. Bout was arrested in Thailand and extradited from there to New York. Russian officials have complained about what they call the growing “practice used by the U.S. of actually hunting down our citizens abroad and arresting them in other nations,” as Grigory Lukyantsev, the Russian Foreign Ministry’s commissioner for human rights, said in August, according to the Russian news outlet RT.
The first former U.S. official said it was highly unlikely that, given the magnitude of his crimes, Mr. Bout would be freed in any deal for Ms. Griner — even if, as some have speculated, the trade were to include Paul Whelan, a former U.S. Marine imprisoned in Moscow since December 2018 on espionage charges. The former official said Russia had sought Mr. Bout’s release in even higher-profile cases in the past and had been firmly rejected.
Both former officials spoke on the condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to discuss their knowledge of Mr. Bout’s case publicly.
Danielle Gilbert, an assistant professor of military and strategic studies at the U.S. Air Force Academy who specializes in hostage diplomacy, agreed that releasing Mr. Bout would be a difficult political proposition. But she did not rule out the idea. “It wouldn’t surprise me if they’re at least considering the possibility,” she said, noting that she does not speak for the U.S. government.
Mr. Bout has at least one advocate for his release in the United States: Shira A. Scheindlin, the judge who presided over his case. In an interview, Ms. Scheindlin said that swapping Mr. Bout for Ms. Griner would be inappropriate, given the scale of his offense in relation to her alleged violation.
But she said a deal that also included Mr. Whelan might even the scales. Mr. Bout has already served 11 years in prison, she noted, saying that “he was not a terrorist, in my opinion. He was a businessman.” Although she was required to impose his mandatory 25-year sentence, she added: “I thought it was too high at the time.”
“So, having served as long as he has, I think the United States’ interest in punishing him has been satisfied,” she said, “and it would not be a bad equation to send him back if we get back these people who are important to us.”
Even if the United States were open to such a deal, Mr. Zissou said it would not be imminent. He said he believed that Russia — which insists Ms. Griner faces legitimate charges and is not a political pawn — was determined to complete her trial before negotiating her release. “And that is likely to take a few months,” he said.