OSOGBO, Nigeria (AP) — Yeyerisa Abimbola has dedicated most of her 58 years on Earth to the Osun, a waterway in deeply religious Nigeria named for the river goddess of fertility. As the deity’s chief priestess, she leads other women known as servants of Osun in daily worship and sacrificial offerings along the riverbank.
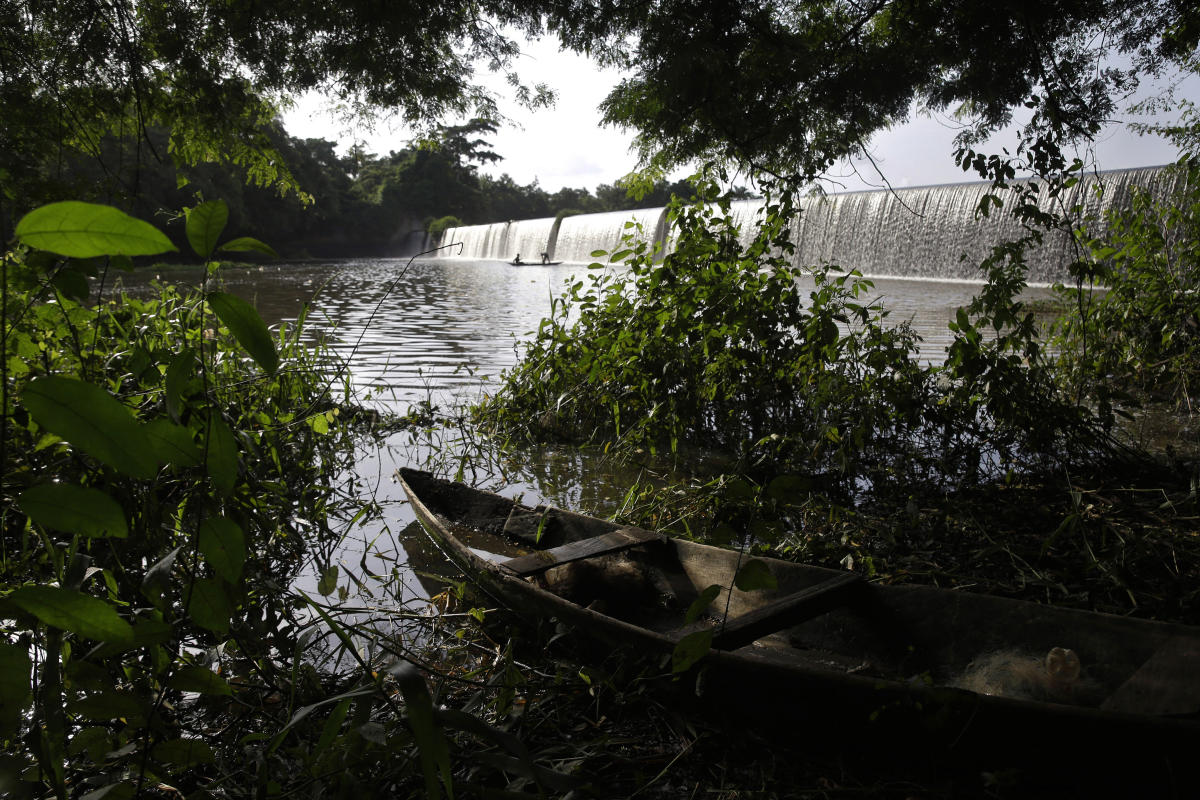
But with each passing day, she worries more and more about the river. Once sparkling and clear and home to a variety of fish, today it runs mucky and brown.
“The problem we face now are those that mine by the river,” Abimbola said. “As you can see, the water has changed color.”
The river, which flows through the dense forest of the Osun-Osogbo Sacred Grove — designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2005 — is revered for its cultural and religious significance among the Yoruba-speaking people predominant in southwestern Nigeria, where Osun is widely worshipped.
But it’s under constant threat from pollution from waste disposal and other human activity — especially the dozens of illegal gold miners across Osun state whose runoff is filling the sacred river with toxic metals. Amid lax enforcement of environmental laws in the region, there are also some who use the river as a dumping ground, further contributing to its contamination.
The servants of Osun, made up of women mostly between the ages of 30 and 60, live in a line of one-room apartments along the side of the Osogbo palace, the royal house of the the Osogbo monarch about 1.5 kilometers (1 mile) north of the grove and river.
They leave behind everything from their secular lives, including marriages, to serve both the goddess and the king. They have little interaction with outsiders, allowing them to devote themselves fully to the goddess, whom they worship daily at a shrine tucked deep inside the grove.
Often seen in flowing white gowns symbolizing the purity the river represents, the women carry out various tasks for the goddess from dawn to dusk, from overseeing sacrificial offerings, mostly live animals and drinks, to carrying out cultural activities in the Osun’s waters. Some say the goddess heals them of afflictions when they drink or bathe in the river, and others say she can provide wealth or fertility.
One servant of Osun, who goes by the name Oluwatosin, said the river brought her a child when she was having difficulties with childbirth. Now the mother of two children, she intends to remain forever devoted to the river and the goddess.
“It is my belief, and Osun answers my prayers,” Oluwatosin said.
The river also serves as an important “pilgrimage point” for Yoruba people in Nigeria, said Ayo Adams, a Yoruba scholar — especially during the Osun-Osogbo festival, a colorful annual celebration that draws thousands of Osun worshippers and tourists “to celebrate the essence of the Yoruba race.” Some attendees say it offers the chance for a personal encounter with the goddess.
But this year, as the two-week August festival neared, palace authorities announced they had been forced to take the unusual step of telling people to stop drinking the water.
“We have written to the state government, the museum on the activities of the illegal miners and for them to take actions to stop them,” said Osunyemi Ifarinu Ifabode, the Osun chief priest.
Osun state is home to some of Nigeria’s largest gold deposits, and miners in search of gold and other minerals — many of them operating illegally — are scattered across swampy areas in remote villages where there is scant law enforcement presence. While community leaders in Osogbo have been able to keep miners out of the immediate area, they’re essentially free to operate with impunity upstream and to the north.
The miners take water from the river to use in exploration and exploitation, and the runoff flows back into it and other waterways, polluting the drinking water sources of thousands of people.
“It is more or less like 50% of the water bodies in Osun state, so the major water bodies here have been polluted,” said Anthony Adejuwon, head Urban Alert, a nonprofit leading advocacy efforts to protect the Osun River.
Urban Alert conducted a series of tests on the Osun in 2021 and found it to be “heavily contaminated.” The report, which was shared with The Associated Press, found lead and mercury levels in the water at the grove that were, respectively, 1,000% and 2,000% above what’s permissible under the Nigerian Industrial Standard. Urban Alert attributes it to many years of mining activity, some of it within 30 kilometers (19 miles) from the river.
Despite the drinking ban issued by the palace, during a recent visit AP witnessed residents trooping to the river daily to fill up gallon containers for domestic use.
Dr. Emmanuel Folami, a physician based in Osogbo, the state capital, said drinking the toxic water or otherwise using it for purposes that risk human exposure is a “big health concern” that could cause lead poisoning.
In March, the Osun state government announced the arrest of “several individuals for illicit mining, seizures and site closures,” and promised it was studying the level of pollution of the river and ways to address it.
But activists question the sincerity and commitment behind such efforts: “If we cannot see the state government taking action within its own jurisdiction as a (mining) license holder, what are we going to say about the other people?” said Adejuwon of Urban Alert, which is running a social media campaign with the hashtag #SaveOsunRiver.
Abimbola, a servant of Osun since she was just 17 years old, said the goddess is tolerant and giving. She thanks Osun for her blessings — a home, children, good health.
“Every good thing that God does for people, Osun does the same,” she said.
Yet she and others warn that even Osun has her limits.
There may be problems if the river remains contaminated and Osun “gets angry or is not properly appeased,” said Abiodun Fasoyin, a village chief in Esa-Odo, where much of the mining takes place, about 40 kilometers (25 miles) east of Osogbo.
“The riverbank will overflow and sweep people away when it is angry,” Abimbola said. “Don’t do whatever she doesn’t want.”
___
Associated Press religion coverage receives support through the AP’s collaboration with The Conversation US, with funding from Lilly Endowment Inc. The AP is solely responsible for this content.