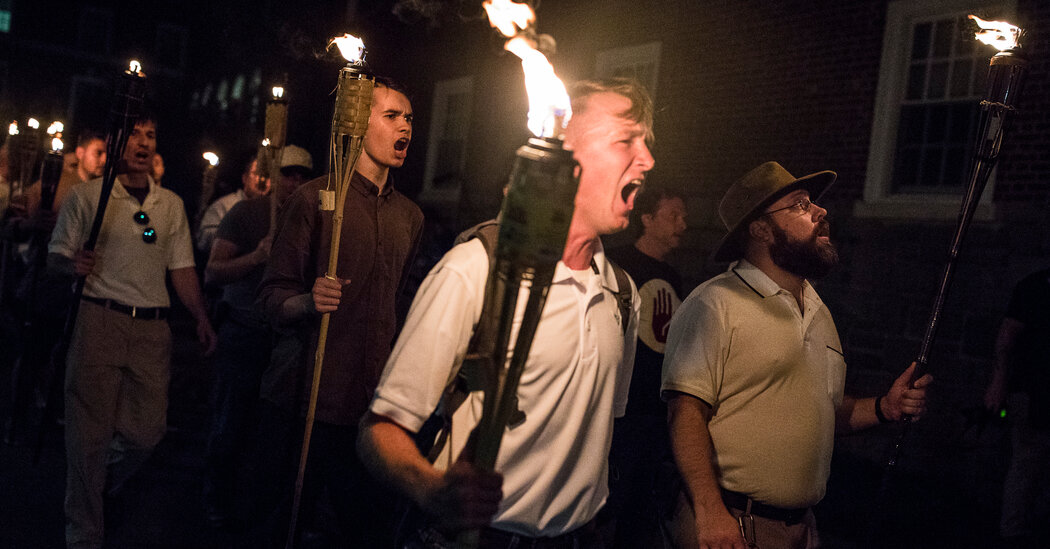Inside a Pittsburgh synagogue in 2018, a white man with a history of antisemitic internet posts gunned down 11 worshipers, blaming Jews for allowing immigrant “invaders” into the United States.
The next year, another white man, angry over what he called “the Hispanic invasion of Texas,” opened fire on shoppers at an El Paso Walmart, leaving 23 people dead, and later telling the police he had sought to kill Mexicans.
And in yet another deadly mass shooting, unfolding in Buffalo on Saturday, a heavily armed white man is accused of killing 10 people after targeting a supermarket on the city’s predominantly Black east side, writing in a lengthy screed posted online that the shoppers there came from a culture that sought to “ethnically replace my own people.”
Three shootings, three different targets — but all linked by one sprawling, ever-mutating belief now commonly known as replacement theory. At the extremes of American life, replacement theory — the notion that Western elites, sometimes manipulated by Jews, want to “replace” and disempower white Americans — has become an engine of racist terror, helping inspire a wave of mass shootings in recent years and fueling the 2017 right-wing rally in Charlottesville, Va., that erupted in violence.
But replacement theory, once confined to the digital fever swamps of Reddit message boards and semi-obscure white nationalist sites, has gone mainstream. In sometimes more muted forms, the fear it crystallizes — of a future America in which white people are no longer the numerical majority — has become a potent force in conservative media and politics, where the theory has been borrowed and remixed to attract audiences, retweets and small-dollar donations.
By his own account, the Buffalo suspect, Payton S. Gendron, followed a lonelier path to radicalization, immersing himself in replacement theory and other kinds of racist and antisemitic content easily found on internet forums, and casting Black Americans, like Hispanic immigrants, as “replacers” of white Americans. Yet in recent months, versions of the same ideas, sanded down and shorn of explicitly anti-Black and antisemitic themes, have become commonplace in the Republican Party — spoken aloud at congressional hearings, echoed in Republican campaign advertisements and embraced by a growing array of right-wing candidates and media personalities.
No public figure has promoted replacement theory more loudly or relentlessly than the Fox host Tucker Carlson, who has made elite-led demographic change a central theme of his show since joining Fox’s prime-time lineup in 2016. A Times investigation published this month showed that in more than 400 episodes of his show, Mr. Carlson has amplified the notion that Democratic politicians and other assorted elites want to force demographic change through immigration, and his producers sometimes scoured his show’s raw material from the same dark corners of the internet that the Buffalo suspect did.
“It’s not a pipeline. It’s an open sewer,” said Chris Stirewalt, a former Fox News political editor who was fired in 2020 after defending the network’s decision to call Arizona for then-candidate Joseph R. Biden, and who wrote a forthcoming book on how media outlets stoke anger to build audiences.
“Cable hosts looking for ratings and politicians in search of small-dollar donations can see which stories and narratives are drawing the most intense reactions among addicted users online,” Mr. Stirewalt said. Social media sites and internet forums, he added, are “like a focus group for pure outrage.”
In just the past year, Republican luminaries like Newt Gingrich, the former House speaker and Georgia congressman, and Elise Stefanik, the center-right New York congresswoman turned Trump acolyte (and third-ranking House Republican), have echoed replacement theory. Appearing on Fox, Mr. Gingrich declared that leftists were attempting to “drown” out “classic Americans.”
In September, Ms. Stefanik released a campaign ad on Facebook claiming that Democrats were plotting “a PERMANENT ELECTION INSURRECTION” by granting “amnesty” to illegal immigrants, which her ad said would “overthrow our current electorate and create a permanent liberal majority in Washington.” That same month, after the Anti-Defamation League, a civil rights group, called on Fox to fire Mr. Carlson, Representative Matt Gaetz, Republican of Florida, stood up both for the TV host and for replacement theory itself.
“@TuckerCarlson is CORRECT about Replacement Theory as he explains what is happening to America,” Mr. Gaetz wrote on Twitter. In a statement after the Buffalo shooting, Mr. Gaetz said that he had “never spoken of replacement theory in terms of race.”
One in three American adults now believe that an effort is underway “to replace native-born Americans with immigrants for electoral gains,” according to an Associated Press poll released this month. The poll also found that people who mostly watched right-wing media outlets like Fox News, One American News Network and Newsmax were more likely to believe in replacement theory than those who watched CNN or MSNBC.
Underlying all variations of replacement rhetoric is the growing diversity of the United States over the past decade, as the populations of people who identify as Hispanic and Asian surged and the number of people who said they were more than one race more than doubled, according to the Census Bureau.
Democratic politicians have generally been more supportive of immigration than Republicans, especially in the post-Trump era, and have pushed for more humane treatment of migrants and refugees. But the number of immigrants living in the United States illegally, which rose throughout the 1990s and 2000s, first began to decline under President Obama, a Democrat whom critics nicknamed the “deporter-in-chief.” There is no evidence of widespread voting by noncitizens and others who are ineligible. And while Mr. Biden has laid out plans to expand legal immigration, federal agencies have expelled more than 1.3 million migrants at the southwest border on his watch, while continuing some of the more restrictive immigration policies begun by former President Trump.
Throughout his presidency, Mr. Trump filled his public speeches and Twitter feed with often inflammatory, sometimes false rhetoric about immigrants, and he employed the term “invaders” in arguing for a border wall. Such language has been more broadly adopted by his most ardent supporters, such as Wendy Rogers, an Arizona state senator, who last summer said on Twitter, “We are being replaced and invaded”by illegal immigrants.
Efforts to reach Ms. Rogers on Sunday were unsuccessful. Reached by email, Mr. Gingrich declared replacement theory “insane,” adding that he was opposed to all anti-Semitism as well as “the white racist violence in Buffalo.”
Responding to criticism of Ms. Stefanik’s ad in the wake of the Buffalo shooting, a senior adviser for the congresswoman sent two responses: a sorrowful statement from Ms. Stefanik about the killing in Buffalo, and a fiery rejoinder from the adviser that “despite sickening and false reporting,” the congresswoman “has never advocated for any racist position or made a racist statement.”
Experts who study digital extremism and media described a complex interplay between the darker version of replacement theory that features on white nationalist or nativist websites, and the attenuated versions now echoing around the conventional right, including on cable news and in pro-Trump media outlets.
“Someone like Carlson can introduce viewers to ideas that they then explore more fully online, searches that lead them into far-right spaces that either reinforce their existing views or radicalize them,” said Nicole Hemmer, a historian at Columbia University. “But someone like Carlson is also important because he legitimates those ideas, making them seem less radical when viewers see them.”
Measuring the extent of Mr. Carlson’s influence in spreading replacement theory may be impossible. But controversies around the host’s use of “replacement” rhetoric appear to have at least helped drive public curiosity about the idea. Until the Buffalo shootings, according to Google data, there had been three big spikes in Google searches for “replacement theory” or “great replacement,” a European variation popularized by the French writer Renaud Camus in recent years. Two followed the shootings in Christchurch, New Zealand, and El Paso, each covered by news outlets around the world. The third came in April 2021, when Mr. Carlson drew calls for Fox to fire him after defending the idea of demographic “replacement” on the network.
The Buffalo suspect appears to have immersed himself on web forums like 4chan and 8chan, where versions of replacement theory abound. That is also where the suspect, before setting out to slaughter Black shoppers in Buffalo, posted a 180-page compendium of racist arguments and internet memes.
He wrote that he got his news from Reddit. He began browsing 4chan in May 2020 “after extreme boredom,” he wrote, and quickly found a gateway to anti-Black and antisemitic replacement content. Reflecting the most extreme versions of replacement theory, the suspect deemed Black people, like immigrants, as “replacers”: people who “invade our lands, live on our soil, live on government support and attack and replace our people.”
According to a detailed analysis by the Anti-Defamation League provided to The Times, the suspect’s screed plagiarized almost two-thirds of another manifesto — the one left by an Australian man who in 2019 murdered dozens of Muslims as they prayed in two mosques in Christchurch. In some instances, the Buffalo suspect replaced the Christchurch killer’s references to Angela Merkel, the former German chancellor, with George Soros, the billionaire philanthropist. One page of the Australian’s document includes a purported count of Jews working at the senior levels of major media outlets, including Fox itself.
Oren Segal, vice president of the ADL’s Center on Extremism, said that the Buffalo suspect’s repurposing of the Christchurch manifesto to justify an attack on Black Americans “demonstrates the evolving and interactive nature of extremist propaganda.”
Mr. Carlson’s replacement rhetoric comes without the explicitly antisemitic elements common on racist web platforms. There is no indication that the Buffalo gunman watched Mr. Carlson’s show, or any other on Fox, and Mr. Carlson has denounced political violence even as he fans his viewers’ fears.
But there are also notable echoes between Mr. Carlson’s segments and the Buffalo suspect’s long litany of grievances, reflecting the blurry boundary between internet-fueled griping and lines of attack now common in conservative media and politics.
“Why is diversity said to be our greatest strength? Does anyone even ask why? It is spoken like a mantra and repeated ad infinitum,” the suspect wrote. The line nearly matches one of Mr. Carlson’s go-to attacks on Fox. “How, precisely, is diversity our strength?” Mr. Carlson asked in a 2018 segment. one of many in which he has hit on the question. “Since you’ve made this our new national motto, please be specific as you explain it.”
A Fox spokeswoman declined to comment.
Amy Spitalnick, the executive director of Integrity First for America, a group that waged a successful civil suit against organizers of the 2017 Charlottesville rally, argued that the broader promotion of replacement rhetoric normalized hate and emboldened violent extremists.
“This is the inevitable result of the normalization of white supremacist Replacement Theory in all its forms,” Ms. Spitalnick said. “Tucker Carlson may lead that charge — but he’s backed by Republican elected officials and other leaders eager to amplify this deadly conspiracy.”
Alan Feuer, Emily Cochrane, Zolan Kanno-Youngs, Chris Cameron and Azi Paybarah contributed reporting.